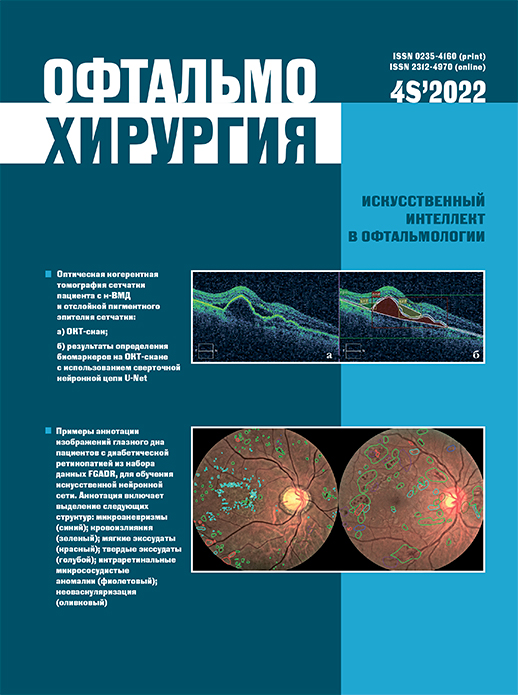
Разработка модели глубокого машинного обучения для обнаружения биомаркеров анатомического и функционального исхода анти-VEGF-терапии на ОКТ-изображениях сетчатки
Ключевые слова:
возрастная макулярная дегенерация, ОКТ, искусственный интеллект, машинное обучение, биомаркеры, анти-VEGF-терапияАннотация
Актуальность. Почти 200 млн человек во всем мире страдают от возрастной макулярной дегенерации (ВМД), 10% случаев которой составляет ее неоваскулярная форма (н-ВМД) – причина тяжелой потери зрения для большинства пациентов. Введение ингибиторов фактора роста эндотелия сосудов (анти-VEGF-терапия) позволяет добиться регрессии процесса неоваскуляризации и сохранить зрение. Тем не менее на сегодняшний день это довольно дорогостоящий метод лечения,
который сопровождается различными осложнениями. Неоваскулярная форма ВМД (н-ВМД) является наиболее распространенной причиной такого осложнения, как разрыв пигментного эпителия (РПЭ). Предикторы анатомического исхода (РПЭ), а также предикторы функционального исхода или конечной остроты зрения могут быть оценены с
помощью оптической когерентной томографии (ОКТ). Для автоматизации процессов выделения морфологических структур на изображениях ОКТ используют методы глубокого машинного обучения.
Цель. Создание алгоритма автоматизированного обнаружения биомаркеров исхода анти-VEGF-терапии пациентов с н-ВМД и РПЭ на снимках ОКТ.
Материал и методы. Для разработки алгоритма сегментации нами был использован набор ретроспективных данных в виде 251 аннотированного изображения ОКТ, полученного при первичном осмотре пациентов, которые проходили лечение н-ВМД с помощью анти-VEGF-терапии с 2014 по 2021 г. Архитектура нейронной сети представляла из себя сверточную нейронную сеть UNET. Для оценки эффективности предлагаемой модели был использован коэффициент Дайса (DSC) Результаты. Точность сегментации показала высокие значения для определения всех биомаркеров – от 0,97 до 0,99. Для отслойки пигментного эпителия сетчатки DSC показывает высокое значение, равное 0,8, для пигментного эпителия и субретинальной жидкости – 0,4, а для остальных биомаркеров – от 0,3 до 0,15.
Заключение. Полученные результаты сегментации ОКТ-изображений показали высокую точность определения пикселей (accuracy). Коэффициент Дайса показал хорошие значения для сегментации отслойки пигментного эпителия сетчатки. Дальнейшие исследования будут направлены на то, чтобы увеличить набор данных для обучения и валидации нейронной сети и повысить точность сегментации для других биомаркеров.
Библиографические ссылки
1. Wong WL, Su X, Li X, Cheung CMG, Klein R, Cheng CY, et al. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Global Health. 2014;2(2): e106–116.
2. Singh SR, Lupidi M, Mishra SB, Paez-Escamilla M, Querques G, Chhablani J. Unique optical coherence tomographic features in age-related macular degeneration. Survey of Ophthalmology. 2020;65(4): 451–457.
3. Rosenfeld PJ, Brown DM, Heier JS, Boyer DS, Kaiser PK, Chung CY, et al. Ranibizumab for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(14): 1419–1431.
4. Schmidt-Erfurth U, Waldstein SM. A paradigm shift in imaging biomarkers in neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016;50: 1–24.
5. Clemens CR, Bastian N, Alten F, Milojcic C, Heiduschka P, Eter N. Prediction of retinal pigment epithelial tear in serous vascularized pigment epithelium detachment. Acta Ophthalmol. 2014;92(1): e50–56.
6. Ying G Shuang, Maguire MG, Daniel E, Ferris FL, Jaffe GJ, Grunwald JE, et al. Association of baseline characteristics and early vision response with 2-year vision outcomes in the comparison of AMD treatments trials (CATT). Ophthalmology. 2015;122(12): 2523–2531.e1
7. Shin HJ, Chung H, Kim HC. Association between foveal microstructure and visual outcome in age-related macular degeneration. Retina. 2011;31(8): 1627–1636.
8. Kwon YH, Lee DK, Kim HE, Kwon OW. Predictive findings of visual outcome in spectral domain optical coherence tomography after ranibizumab treatment in age-related macular degeneration. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2014;28(5): 386.
9. Lee H, Lee M, Kim MA, Chung H, Kim HC. Association of treatment response with quantitative changes in choroidal neovascularization and choroidal vessel in neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Retina. 2020;40(9): 1704–1718.
10. Phadikar P, Saxena S, Ruia S, Lai TYY, Meyer CH, Eliott D. The potential of spectral domain optical coherence tomography imaging based retinal biomarkers. Int J Retin Vitr. 2017;3(1): 1.
11. Chan CK, Abraham P, Meyer CH, Kokame GT, Kaiser PK, Rauser ME, et al. Optical coherence tomography–measured pigment epithelial detachment height as a predictor for retinal pigment epithelial tears associated with intravitreal bevacizumab injections. Retina. 2010;30(2): 203–211.
12. Guber J, Praveen A, Saeed MU. Higher incidence of retinal pigment epithelium tears after ranibizumab in neovascular age-related macular degeneration with increasing pigment epithelium detachment height. Br J Ophthalmol. 2013;97(11): 1486–1487.
13. Leitritz M, Gelisken F, Inhoffen W, Voelker M, Ziemssen F. Can the risk of retinal pigment epithelium tears after bevacizumab treatment be predicted? An optical coherence tomography study. Eye. 2008;22(12): 1504–1507.
14. Chiang A, Chang LK, Yu F, Sarraf D. Predictors of anti-VEGFassociated retinal pigment epithelial tear using fa and oct analysis. Retina. 2008 Oct;28(9):1265–1269.
15. Sarraf D, Chan C, Rahimy E, Abraham P. Prospective evaluation of the incidence and risk factors for the development of RPE tears after high- and low-dose ranibizumab therapy. Retina. 2013;33(8): 1551–1557.
16. Inoue M, Arakawa A, Yamane S, Kadonosono K. Variable response of vascularized pigment epithelial detachments to ranibizumab based on lesion subtypes, including polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Retina. 2013;33(5): 990–997.
17. Cho HJ, Kim KM, Kim HS, Lee DW, Kim CG, Kim JW. Response of pigment epithelial detachment to anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatment in age-related macular degeneration. Am J Ophthalmol. 2016;166: 112–119.
18. Gutfleisch M, Heimes B, Schumacher M, Dietzel M, Lommatzsch A, Bird A, et al. Long-term visual outcome of pigment epithelial tears in association with anti-VEGF therapy of pigment epithelial detachment in AMD. Eye. 2011;25(9): 1181–1186.
19. Panos G, Gatzioufas Z, Petropoulos IK, Dardabounis D, Thumann G, Hafezi F. Effect of ranibizumab on serous and vascular pigment epithelial detachments associated with exudative age-related macular degeneration. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2013;7: 565.
20. Arias L. Treatment of retinal pigment epithelial detachment with antiangiogenic therapy. Clin Ophthalmol. 2010;4: 369.
21. Waldstein SM, Philip AM, Leitner R, Simader C, Langs G, Gerendas BS, et al. Correlation of 3-dimensionally quantified intraretinal and subretinal fluid with visual acuity in neovascular age-related macular degeneration. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016;134(2): 182.
22. Lai TYY, Lai RYK. Association between retinal thickness variability and visual acuity outcome during maintenance therapy using intravitreal anti vascular endothelial growth factor agents for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. J Pers Med. 2021;11(10): 1024.
23. Schmidt-Erfurth U, Chong V, Loewenstein A, Larsen M, Souied E, Schlingemann R, et al. Guidelines for the management of neovascular agerelated macular degeneration by the European Society of Retina Specialists (EURETINA). Br J Ophthalmol. 2014;98(9):1144–1167.
24. Abdelfattah NS, Zhang H, Boyer DS, Rosenfeld PJ, Feuer WJ, Gregori G, et al. Drusen volume as a predictor of disease progression in patients with late age-related macular degeneration in the fellow eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2016;57(4): 1839.
25. Jeng YT, Lai TT, Lin CW, Chen TC, Hsieh YT, Lin CP, et al. The impact of retinal fluid tolerance on the outcomes of neovascular age-related macular degeneration treated using aflibercept: A real-world study. Tsai DC, editor. PLoS ONE. 2022;17(7): e0271999.
26. Kim JH, Sagong M, Woo SJ, Kim YC, Cho H, Lee YH, et al. A realworld study assessing the impact of retinal fluid on visual acuity outcomes in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration in Korea. Sci Rep. 2022;12(1): 14166.
27. Miyata M, Ooto S, Yamashiro K, Tamura H, Uji A, Miyake M, et al. Influence of vitreomacular interface score on treatment outcomes of anti VEGF therapy for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Int J Retina Vitreous. 2021;7(1): 77.
28. Petrachkov DV, Budzinskaya MV, Pavlov VG, Durzhinskaya MH, Khalatyan AS. Neurodegenerative biomarkers of the response to diabetic macular edema treatment. The Russian Annals of Ophthalmol. 2020;136(4): 201.
29. Yoshitake T, Murakami T, Suzuma K, Dodo Y, Fujimoto M, Tsujikawa A. Hyperreflective foci in the outer retinal layers as a predictor of the functional efficacy of ranibizumab for diabetic macular edema. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1): 873.
30. Asai T, Ikuno Y, Nishida K. Macular microstructures and prognostic factors in myopic subretinal hemorrhages. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55(1): 226–232.
31. Tao LW, Wu Z, Guymer RH, Luu CD. Ellipsoid zone on optical coherence tomography: a review: Ellipsoid zone on optical coherence tomography. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2016;44(5): 422–430.
32. Dou N, Yu S, Tsui CK, Yang B, Lin J, Lu X, et al. Choroidal vascularity index as a biomarker for visual response to antivascular endothelial growth factor treatment in diabetic macular edema. J Diabetes Res. 2021;2021: 1–9.
33. Hu K, Shen B, Zhang Y, Cao C, Xiao F, Gao X. Automatic segmentation of retinal layer boundaries in OCT images using multiscale convolutional neural network and graph search. Neurocomputing. 2019;365: 302–313.
34. Keenan TDL, Goldstein M, Goldenberg D, Zur D, Shulman S, Loewenstein A. Prospective, longitudinal pilot study. Ophthalmol Sci. 2021;1(2): 100034.
35. Lee CS, Tyring AJ, Deruyter NP, Wu Y, Rokem A, Lee AY. Deep-learning based, automated segmentation of macular edema in optical coherence tomography. Biomed Opt Express. 2017;8(7): 3440.
36. Bogunović H, Mares V, Reiter GS, Schmidt-Erfurth U. Predicting treat-and-extend outcomes and treatment intervals in neovascular agerelated macular degeneration from retinal optical coherence tomography using artificial intelligence. Front Med. 2022;9: 958469.
37. Fang L, Cunefare D, Wang C, Guymer RH, Li S, Farsiu S. Automatic segmentation of nine retinal layer boundaries in OCT images of nonexudative AMD patients using deep learning and graph search. Biomed Opt Express. 2017;8(5): 2732.
38. Roy AG, Conjeti S, Karri SPK, Sheet D, Katouzian A, Wachinger C, et al. ReLayNet: retinal layer and fluid segmentation of macular optical coherence tomography using fully convolutional networks. Biomed Opt Express. 2017;8(8): 3627.
39. Devalla SK, Renukanand PK, Sreedhar BK, Subramanian G, Zhang L, Perera S, et al. DRUNET: a dilated-residual U-Net deep learning network to segment optic nerve head tissues in optical coherence tomography images. Biomed Opt Express. 2018;9(7): 3244.
40. De Fauw J, Ledsam JR, Romera-Paredes B, Nikolov S, Tomasev N, Blackwell S, et al. Clinically applicable deep learning for diagnosis and referral in retinal disease. Nat Med. 2018;24(9): 1342–1350.
41. Dice LR. Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology. 1945;26(3): 297–302.
42. Zijdenbos AP, Dawant BM, Margolin RA, Palmer AC. Morphometric analysis of white matter lesions in MR images: method and validation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1994;13(4): 716–724.
43. Midena E, Torresin T, Velotta E, Pilotto E, Parrozzani R, Frizziero L. OCT Hyperreflective Retinal Foci in Diabetic Retinopathy: A Semi-Automatic Detection Comparative Study. Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 22;12: 613051.
44. Prahs P, Radeck V, Mayer C, Cvetkov Y, Cvetkova N, Helbig H, et al. OCT-based deep learning algorithm for the evaluation of treatment indication with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor medications. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2018;256(1): 91–98.
45. Rudin C, Chen C, Chen Z, Huang H, Semenova L, Zhong C. Interpretable machine learning: fundamental principles and 10 grand challenges. 2021. Available from: http://arxiv.org/abs/2103.11251 [Assessed 29th November 2022]
Опубликован
Выпуск
Раздел
Категории
Лицензия

Это произведение доступно по лицензии Creative Commons «Attribution-NonCommercial» («Атрибуция — Некоммерческое использование») 4.0 Всемирная.